4 common myths about back pain
There are many myths about back pain and how to care for it that we hear regularly. Here are 4 of the most common:
1). The more severe the pain the more damage there is in my back.
Pain is very complicated and each individual experiences differently. The pain signals received in the brain have little correlation to the level of “damage” in the back. Other factors including the overall health of the person, fatigue, exercise levels and psychological reasons such as stress all have an impact on the perceived pain levels.
2). Resting is the best
Studies show physical activity can help relieve back pain, lying or sitting still is much worse for your back and can often delay recovery. Physical exercise improves muscle strength, increases flexibility and improves blood circulation which aids healing. Regular exercise has also been shown to help prevent back pain.
Your osteopath can give you exercise advice and determine what type of activities are appropriate for your particular problem.
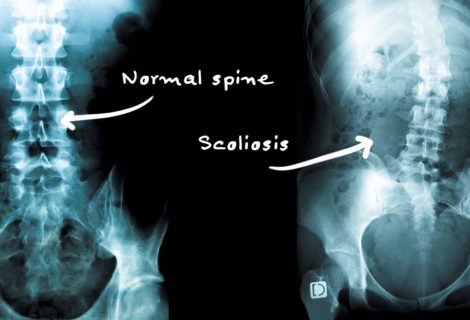
3). I need a scan to find out what is wrong
This is not necessarily the case, often scans such as ultrasound, X-ray or MRI don’t always show what is actually causing the pain. It is common to see abnormalities in the joints but this doesn’t always identify the exact cause of the pain, and sometimes results in more confusion for the person.
Your osteopath will ask questions, do an examination, and take a detailed case history to identify the most likely diagnosis and can refer for the above scans if they deem them to be necessary.
4). I will have to live with it
Again this is another common myth that is not true. Back pain is very common, in fact, around 80% of the population will experience back pain at some point in their lives. However this does not mean that you should just put up with it.
Links to further reading on myths about back pain:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4934575/
http://www.csp.org.uk/your-health/healthy-living/public-information-leaflets/back-pain-myth-busters
https://www.vox.com/science-and-health/2017/8/4/15929484/chronic-back-pain-treatment-mainstream-vs-alternative